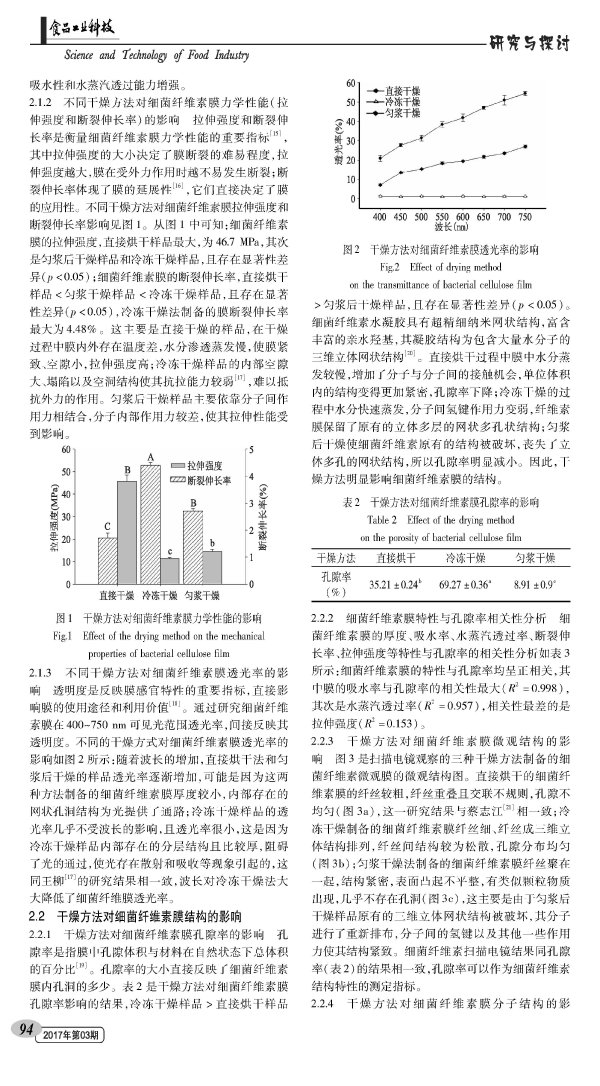
Effect of drying method on the characteristics and structure of bacterial cellulose membrane
Bacterial cellulose refers to a macromolecular polysaccharide obtained by microbial fermentation, which is composed of β-1,4 glycosidic bonds. These polysaccharides have high purity, high mechanical strength, good biocompatibility and degradability. It also has a nano-network structure and is a new non-toxic nano-scale material. Bacterial cellulose has been used in many industrial applications. The most typical applications include environmentally friendly paper cups, paints, body lotions, and oilfield industries. At present, bacterial cellulose is widely used in the field of packaging because of its good mechanical properties, water vapor transmission rate, good moisture resistance and gas barrier properties. In order to meet the demand of bacterial cellulose, more and more scholars have begun to study the preparation of bacterial cellulose membrane and bacterial cellulose composite membrane. For example, Mohammadkazemi studied the effects of different nutrient sources on bacterial cellulose production. Lin studied the effect of high pressure uniform treatment on bacterial fibers. Wei studied the preparation and characteristics of a bacterial cellulose membrane. However, there are relatively few in-depth studies on the specific production process of bacterial cellulose membranes, such as the optimization of membrane drying process and the influence of drying conditions on membrane properties. The drying method of the bacterial cellulose hydrogel varies depending on the application field, and mainly includes methods such as constant temperature electrothermal drying, freeze drying, and electric drying after homogenization. The constant temperature drying method is a new type of drying method. It has the characteristics of fast drying speed, dry product can maintain the original three-dimensional structure state and easy to rehydrate. The drying method after homogenization is to break the original state of the film and then dry it. The method, bacterial cellulose is formed by the absorption of nutrients by microorganisms, and the composition of the formed film varies with the growth of microorganisms and the composition of the medium. The effect of the drying method on the film properties has focused on the effects of different drying parameters on the properties of bacterial cellulose membranes. However, studies on the effects of different drying methods on membrane properties have not been reported. Therefore, the experiment intends to use the constant temperature electric oven to directly dry, homogenate flow, electrothermal drying and freeze drying three methods to treat bacterial cellulose hydrogel, to obtain bacterial cellulose dry film, to explore the different treatment methods for bacterial cellulose membrane structure and The characteristics (mechanical properties, transparency, water vapor transmission rate), the advantages and disadvantages of the performance of the bacterial cellulose membranes prepared by the three drying methods, and the relationship between the membrane structure and its properties, the bacterial cellulose The theoretical basis for the in-depth study of membranes and reagent applications.