Milking method
Milking method: The milner takes a small bench and sits at the rear 1/3-1/2 of the right side of the cow, and is at an angle of 50-60 degrees with the longitudinal axis of the cattle body. To clamp the tank between the two thighs, the left knee is near the anterior side of the right femoral joint of the cow, and the legs are open to the side (character), and milking can begin. Dairy cows have 4 teats. Usually, they squeeze the teats on the front side. This is called "two-way milking method." In addition, there are one-way (first squeeze the side of the two teats), cross-over (one after the teat) and single milking milking method, only in special circumstances apply. When milking, it is necessary to hold the teat with all the fingers of the hand. From the bottom of the hand, you can barely see the teat, and use all your fingers and joints at the same time. This is called fist gripping or squeezing. The advantage of this method is that it can keep the cow's teat clean, dry, not damaged, deformed, milking fast, saving energy and convenience.
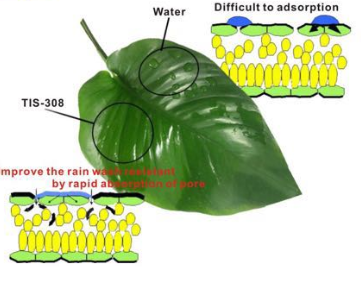
Wetting Agent is anionic special surfactant compound products, which widely used in SC, EW, EC and OD formulation.
With wetting, rapid penetrating property ,improve the quick effect.Product is anionic, the compound is good, it can be used in water-based pesticides, also in oil-based pesticide.
We also name it penetrator. It can used in wide PH 4-8.
Wetting Agent Wetting Agent,Wetting Penetrating Agent,Wetting Adjuvant,Agricultural Wetting Agent Jiangxi Tiansheng New Materials Co.,Ltd , https://www.jxtsxcl.com
1) Press milking method: The lower end of the fist should be flush with the free end of the teat so as not to splash the milk and contaminate it. Grip force is generally 15-20 kg, try hard to evenly. The milking speed should be 80 to 20 times per minute, especially when the mother's milk is fast, and the milking speed should be 80-90 times in the first minute of milking; afterwards, with a lot of milk, the speed It is added to 120 times per minute; the last row of milk is less, the speed is restored to 80-90 times per minute; the milking amount per minute should be able to reach 1-1.5 (2.0) kg.
2) Squeezing milking method: For cows with short nipples, milking can be done by fingering or squeezing. That is, with the thumb and forefinger covering the neck of the teat, slide it downwards to remove the milk. This method is easy to operate at the time of beginner, but it is harmful to the breast and can cause the teat to break, the teat to become long, and the teat cavity to bend. This method requires the use of lubricants to reduce the friction between the fingers and the skin of the teat. Milk is the most convenient lubricant, but it increases the chance of contaminating the milk.
When most of the milk has been squeezed, the breasts should be massaged again and a half-side massage of the breasts should be performed, ie massage the right and left breast areas of the breasts separately. The action is from top to bottom with both hands. From the outside to the side, press the side of the two milk areas, and use a little heavier force. Repeat this for 6-7 times so that the milk in the breast flows to the milk pool, and then the various milk areas are repeatedly extracted. At the end of the milking session, a third massage of the breasts is performed. This time, a full massage must be performed. In particular, it is better done for the new breed of cattle by massaging the four milk areas one by one, until they are completely squeezed. After squeezing, the teat can be coated with oil (petrolatum) to prevent cracking of the teat. During each massage, put the milking bucket aside to prevent cow hair, dander, and other dirt from falling into the barrel while contaminating the milk.
In order to ensure good milking, it is also important to note:
The speed of milking is faster: The discharge of milk is the reaction of the milk gland to the action of oxytocin. As a result, the milk is drained from the milk pool and the large milk conduit and the oxytocin can be released from the anterior pituitary to the bloodstream. However, the concentration of oxytocin in blood can only last about 30 minutes. Other tests have shown that within 20-60 seconds after the teat is stimulated, contraction of mammary myoepithelial cells occurs, and a second release of oxytocin can be induced at the same time, but it is harder than the first release, and it is generally not complete. reaction. When oxytocin is released, the rate of milk discharge changes over time, regardless of the amount of breast milk retained in the breast. The reason may be due to fatigue of myoepithelial cells or due to inactivity of oxytocin. In fact, oxytocin is half active in the blood, and it takes only 1-2 minutes until it completely loses its activity, and oxytocin has only 6-8 minutes to function. Therefore, when oxytocin induces contraction of myoepithelial cells, it must be milked as soon as possible. Since the myoepithelial cells also have a contractile response to mechanical stimuli, the breast's hot compresses and massage during milking can also squeeze out some milk extra.
Therefore, after the breasts are heated and scrubbed before milking, the milk must be squeezed within a few minutes (usually 6-10 minutes) and the milk must not be stopped in the middle. If the time is too long and the reflex activity has passed, the milk will stay in the breast and it will be difficult to squeeze out. This will have to reduce the amount of milk produced, which is generally reduced by 10% to 12%.
Obey the milking regulations and prevent the release of milk:
During milking, any unpleasant external stimuli will be transmitted through the sympathetic nervous system, secreting adrenaline into the blood from the adrenal medulla. Because epinephrine has a strong vasoconstrictive ability, it reduces the blood supply to the breast. Therefore, a sufficient amount of oxytocin is prevented from reaching myoepithelial cells and causing it to contract. There is also evidence that epinephrine also directly inhibits the effect of myoepithelial cells on oxytocin. This reflexive inhibition may also occur when the breast is filled with milk, in which case the blood flow in the capillaries is reduced, so that oxytocin cannot reach the myoepithelial cells. Before the emergence of reflexes, the disturbance of the herd may also hinder the release of oxytocin in the posterior pituitary. If this hormone can be injected from the outside world at this time, it can still cause the contraction of myoepithelial cells because there is no contraction of the capillaries caused by epinephrine. In the first cow that has just given birth, the suppression of milking reflex may occur when the cow is first introduced into the milking parlour, but oxytocin injections can be corrected.
Based on the above reasons, the milking time must be strictly enforced, and the work should be performed in a certain order. It should not be disrupted or changed arbitrarily. The milker should concentrate on milking, prohibiting squeaking, noisy and special noise, and keeping the milking environment quiet and comfortable. For gentle cows with kicking, the attitude should be mild, and kicking is strictly prohibited. In this kind of cow, if the milker can keep calm, the cow will keep quiet. When milking, pay attention to the right hind leg of the cow. If you find that the cow wants to lift the right hind leg, you can quickly block it with your left hand. When you have to, you can use the rope to pick up the two hind legs and then milk it again. Be eliminated.
Prevent the occurrence of mastitis:
Mastitis is an inflammatory reaction to the bacterial tissue, chemical, thermal, and mechanical trauma that occurs in the breast tissue. It is manifested by an increase in the amount of protein in the blood and in white blood cells in milk tissue and milk. The purpose is to reduce unhealthy stimulation, repair damaged tissue, and restore the function of the mammary glands. About 5%-10% of the cows in the herd may produce abnormal milk at any time, 40% of which may be caused by pathogenic microorganisms infected with more than 2 teats. The bacteria that cause mastitis include Streptococcus gravis and Staphylococcus aureus. In addition, mononuclear bacteria and Escherichia coli also cause mastitis problems.
Mastitis infections can reduce the amount of milk produced, but it can cause necrosis of breasts and teats, and even cause the cattle to lose productivity and die. Prevention is a key measure to control the incidence of mastitis. Before milking, the hands of the milker should be thoroughly cleaned in disinfectant soapy water, and the cows that have contracted mastitis should be finally milked. Before normal milking, we must first observe the appearance of the breast to see if there is swelling and heat pain. Secondly, we must squeeze the first two milk into a small cup to observe whether there is “milk residueâ€, and for the mother who has aura of mastitis. For cattle, use a separate towel to scrub the breasts. After milking, the teat should be soaked in disinfectant immediately.